MatrixOne v24.2.0.0 Release Notes
We are thrilled to announce the release of MatrixOne v24.2.0.0 on 2024/11/01!
What is Matrixone?
MatrixOne is an AI-driven, cloud-native, hyper-converged database that uses a storage-compute separation architecture and fully leverages cloud infrastructure. It is MySQL-compatible and supports hybrid workload scenarios, combining vector data types and full-text search to efficiently handle multimodal data query and management needs for generative AI applications.
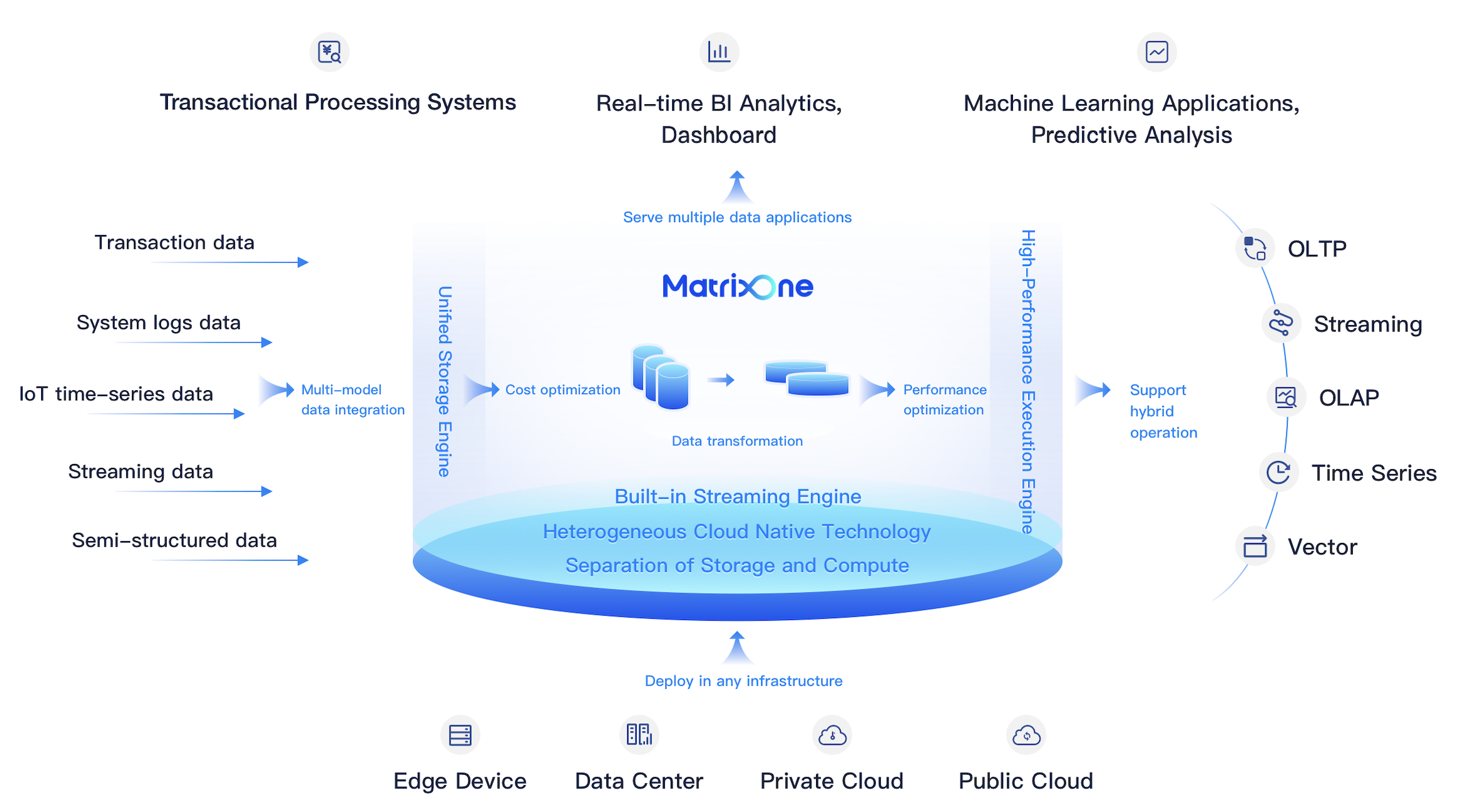
Feature overview
In this new version, MatrixOne provides additional features for AIGC applications, along with significant improvements in enterprise-grade high availability and disaster recovery.
This iteration brings substantial enhancements to MatrixOne's support for generative AI applications, disaster recovery, and system stability. Key features include access to data on external storage, capabilities for handling unstructured data, full-text search functionality, improved vector search performance, support for snapshot backups and point-in-time recovery (PiTR), CDC, and disaster recovery through log-based replication for primary-standby clusters. Additionally, compatibility with MySQL has been further enhanced. With these new features, MatrixOne is steadily becoming an ideal choice for enterprises building AI-driven intelligent data management platforms.
Application scenarios
MatrixOne is suitable for the following application scenarios. We warmly invite users with the following business challenges and needs to contact us for trial testing.
Generative artificial intelligence scenarios
MatrixOne hyper-converged database offers robust multimodal data support, real-time retrieval, and intelligent data processing capabilities for Generative AI, establishing a core infrastructure for such applications. In multimodal scenarios like text and image generation, MatrixOne ensures rapid response and high-quality generation on large datasets through efficient data management, vector and hybrid search, data cleansing and preprocessing supported by Python UDFs, and GPU-accelerated real-time inference. Whether for large-scale data access and storage, online inference, or dynamic feedback, MatrixOne provides stable, low-latency support for Generative AI applications, enabling enterprises to swiftly implement, iterate, and optimize AI-driven innovation.
Time series data application scenarios
In modern IoT applications, billions of devices and sensors continuously collect and transmit data from industrial production lines, smart grids, smart city infrastructure, autonomous vehicles, and more, generating TBs of real-time data daily. MatrixOne hyper-converged database provides efficient real-time data processing for IoT scenarios, supporting millisecond-level high-concurrency writes and rapid retrieval with excellent scalability to handle peak loads. Its real-time analytics enable enterprises to quickly derive critical insights from vast IoT data, seamlessly integrating with machine learning models to directly stream real-time data into models for prediction and anomaly detection. This makes it ideal for applications such as predictive maintenance, energy efficiency optimization, and intelligent monitoring, fully meeting IoT application requirements for high throughput, low latency, and intelligent data management.
Mixed load type application support
In enterprise systems like OA, ERP, and CRM, the growth in data volume and business complexity often makes it challenging for traditional single-node databases to meet peak performance demands, especially during critical periods like month-end or quarter-end. At these times, frequent analysis and real-time statistical reporting are essential for decision-making support. Many companies address this by configuring independent analytical databases or adopting database sharding to alleviate query load on the primary database. However, MatrixOne's support for hybrid workloads enables enterprises to fulfill both operational and analytical needs within a single database, eliminating the need for additional systems. Real-time data analytics allows for quick responses even under high concurrency, while MatrixOne's scalability enables seamless expansion as business needs grow, maintaining efficient real-time querying and reporting even with large data volumes. This ensures that data-driven decision-making remains real-time, continuous, and efficient, significantly enhancing flexibility in data management.
Enterprise-level SaaS scenario
With the rapid growth of enterprise-level SaaS applications, SaaS development must address the needs of a multi-tenant model. Traditional solutions typically choose between a shared database instance for multiple tenants and a dedicated instance per tenant, leading to trade-offs between management costs and tenant isolation. MatrixOne natively supports a multi-tenant architecture, providing load isolation and independent scalability for each tenant along with unified management capabilities. This architecture effectively reduces management costs, ensures data isolation, and improves operational efficiency, fully meeting SaaS applications' demands for cost control, simplified management, and isolation. This makes MatrixOne an ideal database choice for SaaS applications.
Key new features
Multi-mode data management capabilities
MatrixOne supports direct access to external object storage, remote file systems, and local file systems through the Stage object, as well as direct file access on storage systems via the datalink type. This capability is highly beneficial for building data pipelines in generative AI applications with MatrixOne, significantly improving development efficiency and reducing application maintenance costs.
Full-text indexing for text or JSON type data
Creating full-text indexes on JSON or TEXT columns in tables can effectively enhance MatrixOne's performance in AIoT applications. Leveraging MatrixOne's JSON data type can further reduce data redundancy, thereby strengthening MatrixOne's competitiveness in AIoT scenarios.
Vector search
In this iteration, MatrixOne has optimized its vector search capabilities, enabling rapid vector distance-based retrieval within large-scale vector datasets. This efficient retrieval is especially critical for generative AI applications based on large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technologies.
Snapshot-based backup and recovery
Creating data snapshots for clusters or tenants allows the database's state at a specific moment to be quickly captured, ensuring rapid recovery in case of failure or emergency. Snapshot technology has minimal impact on system performance while guaranteeing data consistency for complete recovery. It also supports cross-tenant restoration, enhancing the system's disaster recovery capabilities.
Disaster recovery of active and standby clusters based on log replication
Using a log replication mechanism to synchronize transaction logs from the primary database to the standby database enables high availability and disaster recovery for the primary-standby cluster. When the primary database encounters a failure, the standby database can quickly take over, ensuring uninterrupted business operations.
Point-in-time recovery capabilities
By recording all data changes after the initial snapshot, this feature allows users to restore the database to a precise historical moment in the event of failure, accidental operations, or data corruption, preventing the loss of important information. Compared to traditional full backups, it significantly reduces storage costs and improves recovery efficiency. This feature provides flexibility and security for critical business scenarios, enabling rapid recovery to meet business continuity and compliance requirements.
MatrixOne to MySQL CDC
By capturing changes in the MatrixOne database and synchronizing them in real-time to downstream MySQL, data disaster recovery from MatrixOne to MySQL is achieved. This allows users migrating from MySQL to MatrixOne to maintain a disaster recovery link.
Table-level publish-subscribe functionality
In previous iterations, we supported database-level publish/subscribe, and this iteration further implements more granular table-level publish/subscribe. When data changes occur, table-level publish/subscribe can real-time sync data changes from specific tables to subscribers without exposing information from other tables, providing greater flexibility and control compared to database-level publish/subscribe.
Other new features
SQL statements
- Support rename table
- Support create pitr
- Support drop pitr
- Support alter pitr
- Support restore pitr
- Support show pitrs
- Optimized show publications
- Optimized show subscriptions
- The load data infile command supports loading data in the order of user-specified column names.
Data type
- Support datalink data type
Indexes and constraints
- Add full text index (fulltext Index)
Functions and operators
- Support json_row, jq, try_jq, json_extract_string, json_extract_float64 functions for json data type
- Support addition or subtraction of the date returned by the now() function
Tools
- mo-backup: supports management of pitr
- mo_cdc: supports management of cdc tasks
MySQL Compatibility
- Support Encode()/Decode() function
Quick start
Community users and enterprise developers can deploy MatrixOne for trial use with the following command.
docker pull matrixorigin/matrixone:2.0.0
This documentation site also provides detailed architectural descriptions, installation guides, and development tutorials to help you explore the capabilities of MatrixOne. Additionally, you are welcome to ask questions, discuss, or provide feedback on our website at https://github.com/matrixorigin/matrixone and in our community WeChat group.
Known Issues
- In the current disaster recovery solution for the active and standby clusters, the standby cluster does not support synchronization of data in external tables and stages.
- In the current disaster recovery solution for the active and standby clusters, the standby cluster only supports cold backup and cannot be opened in read-only mode.
- CDC only supports table-level data synchronization.
- Snapshot backup currently only supports cluster and tenant level backup, but can be restored to the cluster, tenant, database or table level.
- Snapshots and PITR backups cannot recover deleted tenant data.
More detailed update log
https://github.com/matrixorigin/matrixone/compare/v1.2.0...v2.0.0